Notes on Metal¶
Presentation¶
When looking for a rigid substance, metal is a good choice compare to stone, wood, glass, ceramic, plastic. The rigidity is relevant when designing parts with the solid mechanics. In this matter, shapes and dimensions are considered invariant, regardless of the strength, pressure, collision and temperature conditions.
Metal overview¶
Rigidity¶
| Material | Young’s modulus | Yield stress | Yield strain | Thermal expansion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | GPa | MPa | % | 10**-6/°C |
| Iron (Fe) | 196 | 80 | 0.04 | 11.8 |
| cast iron | 83 | 400 | 0.4 | 10.5 |
| Steel | 204 | 1450 | 0.7 | 17 |
| Aluminium (Al) | 69 | 95 | 0.13 | 23.1 |
| Aluminium alloy | 75 | 470 | 0.64 | |
| Copper (Cu) | 124 | 33 | 0.03 | 17 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 78 |
Example of thermal expansion:
An iron-part with a width of 10 cm gets longer of 11.8 um when the temperature increases of 10 °C.
Example of limit of elasticity:
An iron-part under strength with a width of 10 cm gets longer of 200 um before getting a plastic deformation.
Auxiliary¶
| Material | Molar mass | Specific volume | Specific heat | Thermal conductivity | Electrical resistivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | kg/mol | m3/kg | J/(kg.K) | W/(m.K) | Ohm.m |
| Iron (Fe) | 0.05584 | 127.0 * 10**-6 | 444 | 80.4 | 9.70 * 10**-8 |
| Aluminium (Al) | 0.02698 | 370.4 * 10**-6 | 897 | 237 | 2.65 * 10**-8 |
| Copper (Cu) | 0.06354 | 111.6 * 10**-6 | 385 | 384.1 | 1.68 * 10**-8 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 0.06539 | 140.0 * 10**-6 | 380 | 116 | 5.90 * 10**-8 |
Energy for fusion¶
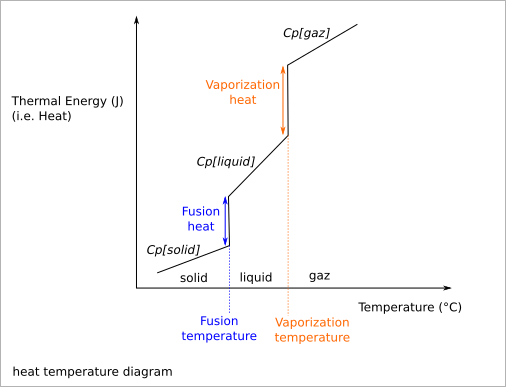
At 101325 Pa (normal atmospheric pressure)
| Material | Cp [solid] | Fusion Tc | Fusion heat | Cp [liquid] | Boiling Tc | Vaporization heat | Cp [gaz] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | J/(kg.K) | °C | J/kg | J/(kg.K) | °C | J/kg | J/(kg.K) |
| Water (H2O) | 2108 | 0 | 334000 | 4187 | 100 | 2264705 | 1996 |
| Nitrogen (N2) | -210 | 25700 | -196 | 200000 | 1025 | ||
| Iron (Fe) | 444 | 1538 | 247134 | 820 | 2861 | 6214000 | |
| Aluminium (Al) | 897 | 660.3 | 396590 | 1180 | 2519 | 10859000 | |
| Copper (Cu) | 385 | 1084.6 | 206170 | 490 | 2562 | 4721000 | |
| Zinc (Zn) | 380 | 419.5 | 112402 | 907 | 1819000 |
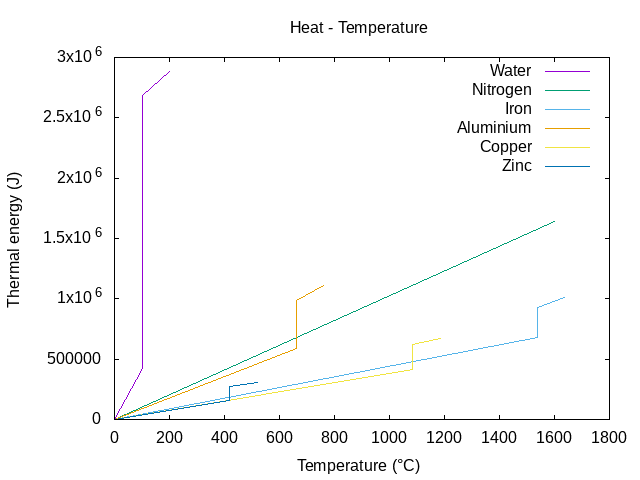
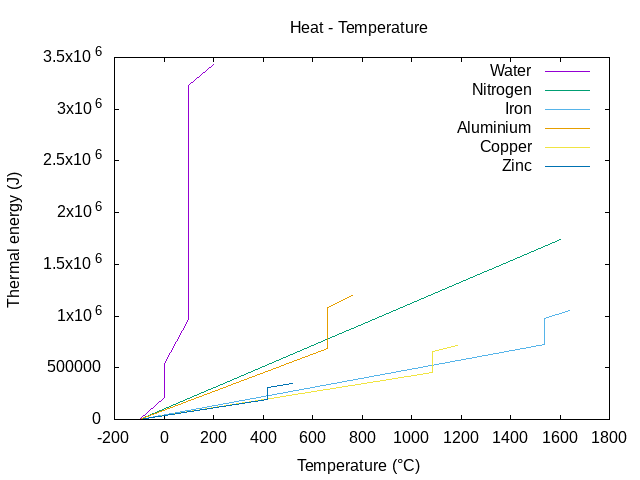
Energy to melt 1 kg of metal:
Water-steam : 100 * 4187 + 2264705 = 2683405 J <=> 0.745 kW/h
Iron : 1538 * 444 + 247134 = 930006 J <=> 0.258 kW/h
Aluminium : 669 * 897 + 396590 = 996683 J <=> 0.276 kW/h
Copper : 1084 * 385 + 206170 = 623510 J <=> 0.173 kW/h
Zinc : 419 * 380 + 112402 = 271622 J <=> 0.075 kW/h
Reminder:
\[1 bar = 100000 Pa\]
\[1 Pa = 1 Nm^{-2} = 1 J m^{-3}\]
\[1 cal = 4.1855 J\]
\[1 mol = 6.022 * 10^{23}\]
Auxiliary table¶
| Material | Molar mass | Specific volume | Thermal conductivity | Electrical resistivity | Magnetic permeability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | kg/mol | m3/kg | W/(m.K) | Ohm.m | H/m |
| Ice (H2O) | 0.018 | 0.00109 | |||
| Water (H2O) | 0.018 | 0.00100 | 0.6 | 20 | 0.99 |
| Steam (H2O) | 0.018 | 1.24 | |||
| Nitrogen (N2) | 0.02802 | 0.799 | 0.026 | 10**9 | 1.00 |
| Iron (Fe) | 0.05584 | 127.0 * 10**-6 | 80.4 | 9.70 * 10**-8 | 5000 |
| Aluminium (Al) | 0.02698 | 370.4 * 10**-6 | 237 | 2.65 * 10**-8 | 1.00 |
| Copper (Cu) | 0.06354 | 111.6 * 10**-6 | 384.1 | 1.68 * 10**-8 | 0.99 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 0.06539 | 140.0 * 10**-6 | 116 | 5.90 * 10**-8 | 0.99 |